______ END ______
| DAU - DAU Glossary of Defense Acquisition Acronyms and Terms | Reference | 2022 |
| The structure of components, their relationships, and the principles and guidelines governing their design and evolution over time. |
| Facts, characteristics, and concepts that define the structure of a system and the interrelationships between its parts and its environment. The data is created in a manner suitable for communication, interpretation, or processing by humans or by automatic means. For complex systems, a framework of conventions, principles and practices is used for organizing and presenting the architecture data within a specific domain of application or community of stakeholders. |
| An existing product, material, component, subsystem, or system sold or traded to the general public during normal business operations at prices based on established catalog or market prices. |
| The use of computers to aid in the software engineering process. CASE tools may include the application of software tools to software design, requirements tracing, code production, testing, document generation, and other software engineering activities. Assemblers and compilers are CASE tools. |
| An aggregation of hardware, software, or both, that is designated for configuration management and treated as a single entity in the configuration management process. The entity within a configuration satisfies an end use function and that can be uniquely identified at a given reference point. |
| A characteristic that analysis indicates is likely, if defective, to create or increase a hazard to human safety, or to result in failure of a system to perform a required function. |
| Those aspects of a systems capability, operational, or technical and other aspects that must be questioned before a systems overall suitability can be known. Critical issues are of primary importance to the decision authority in reaching a decision to allow the system to advance into the next phase of development. |
| A relative measure of the consequences of a failure mode and its frequency of occurrence. |
| Qualitative and quantitative aspects of physical and functional characteristics of a component, device, product, or system that are input to its design process. Design parameters determine cost, design, and risk tradeoffs in the items development. |
| An artifact produced within, or generated from, the digital engineering ecosystem. These artifacts provide data for alternative views to visualize, communicate, and deliver data, information, and knowledge to stakeholders. |
| An integrated digital approach that uses authoritative sources of systems data and models as a continuum across disciplines to support lifecycle activities from concept through disposal. |
| The interconnected infrastructure, environment, and methodology (process, methods, and tools) used to store, access, analyze, and visualize evolving systems data and models to address the needs of the stakeholders. |
| The communication framework that allows a connected data flow and integrated view of an asset’s data (i.e., its Digital Twin) throughout its lifecycle across traditionally siloed functional perspectives. |
| A digital twin is a virtual representation of real-world entities and processes, synchronized at a specified frequency and fidelity. |
| Engineering effort directly related to specific end products. |
| The final production product when assembled, or completed, and ready for issue or deployment. |
| The documentation by which a proposed engineering change is submitted to the responsible authority recommending that a change to an original item of equipment be considered, and the design or engineering change be incorporated into the article to modify, add to, delete, or supersede original parts. |
| The joining of the major sections to perform a complete unit. |
| The formal examination of functional characteristics of a configuration item, or system, to verify that the item has achieved the requirements specified in its functional and/or allocated configuration documentation. |
| A condition that exists when two or more items possess such functional and physical characteristics as to be equivalent in performance and durability, are capable of being exchanged one for the other without alteration on the items themselves or of adjoining items, except for adjustment, and without selection for fit and performance. |
| The functional and physical characteristics required to exist at a common boundary or connection between persons, between systems, or between persons and systems. A system external to the system being analyzed that provides a common boundary or service that is necessary for the other system to perform its mission in an undergraded mode, e.g., a system that supplies power, cooling, heating, air services, or input signals. |
| A management process applied throughout the life of a system that bases all programmatic decisions on the anticipated mission-related and economic benefits derived over the life of the system. It includes the implementation, management, and oversight by the designated Program Manager (PM) of all activities associated with the acquisition, development, production, fielding, sustainment, and disposal of a DoD system across its life cycle. |
| An operation in the construction of a section that joins a number of subassemblies. |
| The process of making an item using machinery, often on a large scale, and with division of labor. |
| A structured evaluation of a technology, component, manufacturing process, weapon system or subsystem using Manufacturing Readiness Levels (MRLs). It is performed to define the current level of manufacturing maturity, identify maturity shortfalls and associated costs and risks and to provide the basis for manufacturing maturation and risk management. |
| A measure used to assess the maturity of a given technology, component or system from a manufacturing prospective. The purpose of MRLs is to provide decision makers at all levels with a common understanding of the relative maturity and attendant risks associated with the manufacturing technologies, products, and processes under consideration. There are ten MRLs, with MRL 1 being the least mature and MRL 10 being the most mature. |
| Data about data. For example, the file name is meta data about a CAD design held as a file. |
| The portion of the data set that contains model geometry and supplemental geometry. | 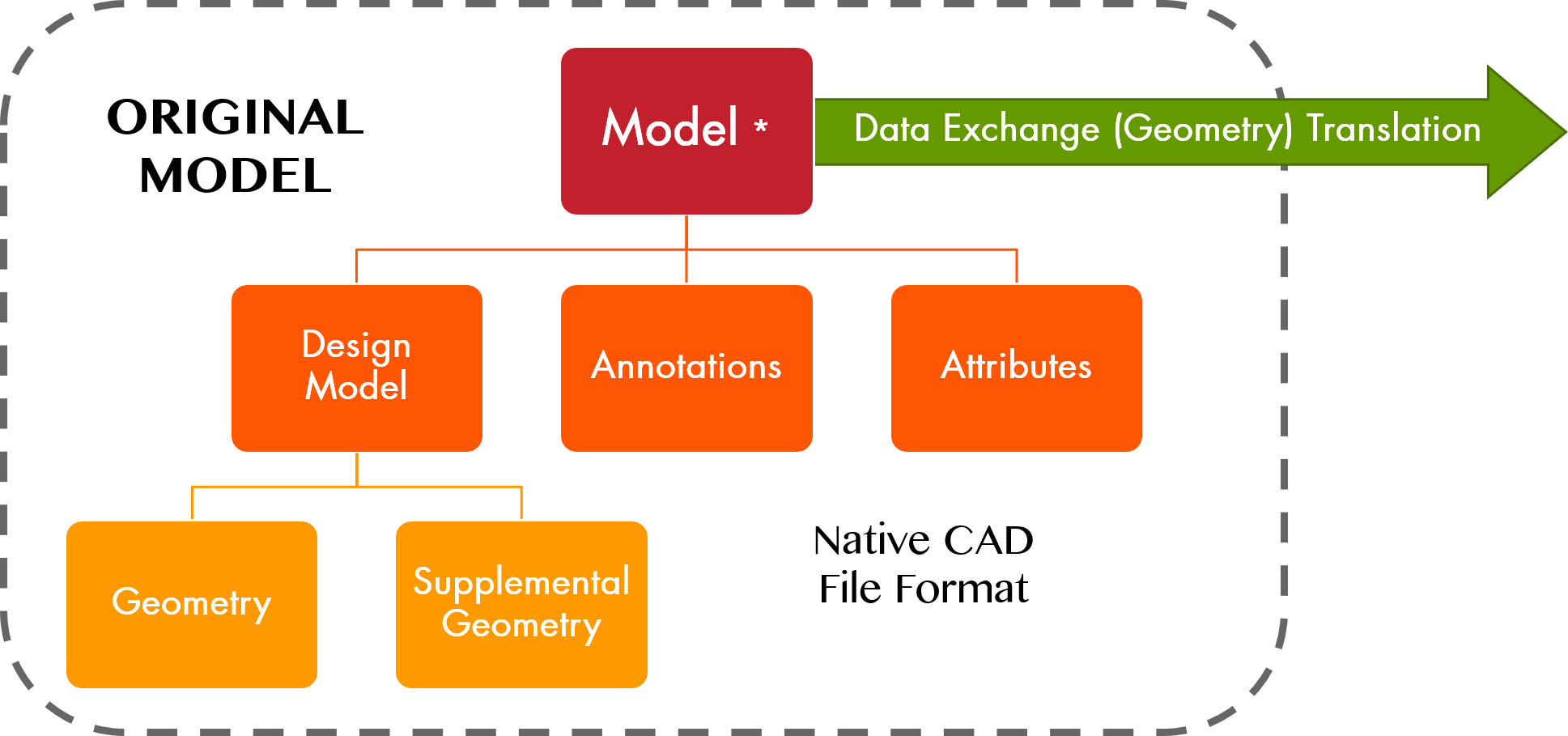 |
| Widely accepted and supported standards set by recognized standards organizations or the marketplace. These standards support interoperability, portability, and scalability and are equally available to the public at no cost or with a moderate license fee. |
| A system whose technical architecture adopts open standards and supports a modular, loosely coupled, and highly cohesive system structure. This modular open architecture includes publishing of key interfaces within the system and relevant design disclosure. |
| A work statement for performance-based acquisitions that describes the required product or service in clear, specific and objective terms with associated measurable outcomes. |
| Physical examination of the actual configuration of the item being produced. It verifies that the related design documentation matches the item as specified in the contract. The system product baseline is finalized and validated at the PCA. |
| A single piece not normally subject to disassembly without destruction or impairment of use, such as resistors, transistors, relays, and gears. |
| Product Definition Data, Technical Data, Item, Feature, Drawing, Item. IdentificationIncludes materials, parts, components, subassemblies, assemblies, and equipment. The term product shall also encompass a family of products. |
| The effective use of resources to produce, on schedule, the required number of end units that meet specified quality, performance, and cost. It includes, but is not limited to, industrial resource analysis, producibility assessment, producibility engineering, and planning, production engineering, industrial preparedness planning, post-production planning, and productivity enhancement. |
| The state, condition, or preparedness of a system to proceed into production. A system is ready for production when the producibility of the production design and the managerial and physical preparations necessary for initiating and sustaining a viable production effort have progressed to the point where a production commitment can be made without incurring unacceptable risks that will breach thresholds of schedule, performance, cost, or other established criteria. |
| A planned and systematic pattern of all actions necessary to provide confidence that adequate technical requirements are established, that products and services conform to established technical requirements, and that satisfactory performance is achieved. |
| The effectiveness of the design and manufacturing functions in executing the product manufacturing requirements and process specifications while meeting tolerances, process control limits, and target yields for a given product group. |
| A first level refinement of one or more capability requirements identified in an Information Systems - Initial Capabilities Document (IS-ICD) or Information Systems - Capability Development Document (IS-CDD), and is co-developed by the operational user (or representative) and the program office. The RDP (or equivalent) identifies the Key Performance Parameters (KPPs), including the Net-Ready KPP, Key System Attributes (KSAs), and Additional Performance Attributes (APAs) necessary to scope and cost implementation of a capability solution. The RDP (or equivalent) may also identify non-material changes that need to be implemented to fully realize the IS capability solution. The RDP (or equivalent) is approved by the delegated oversight authority listed in the IS-ICD or IS-CDD. |
| The design of a system such that its performance is insensitive to variations in manufacturing tolerances, or its operational environment (including maintenance, transportation, and storage), or to component drift as a result of aging. |
| A grouping of elements that are closely related and often physically interface. These include configuration items (CIs) produced by several contractors and integrated by one contractor. |
| A concept that envisions greater and more integrated use of Modeling and Simulation (M&S) in the acquisition process. DoD and industry would be enabled by robust, collaborative use of simulation technology that is integrated across acquisition programs and phases. |
| A document that describes essential technical requirements for material and the criteria for determining whether those requirements are met. |
| A document that establishes technical criteria, methods, processes, and practices. | 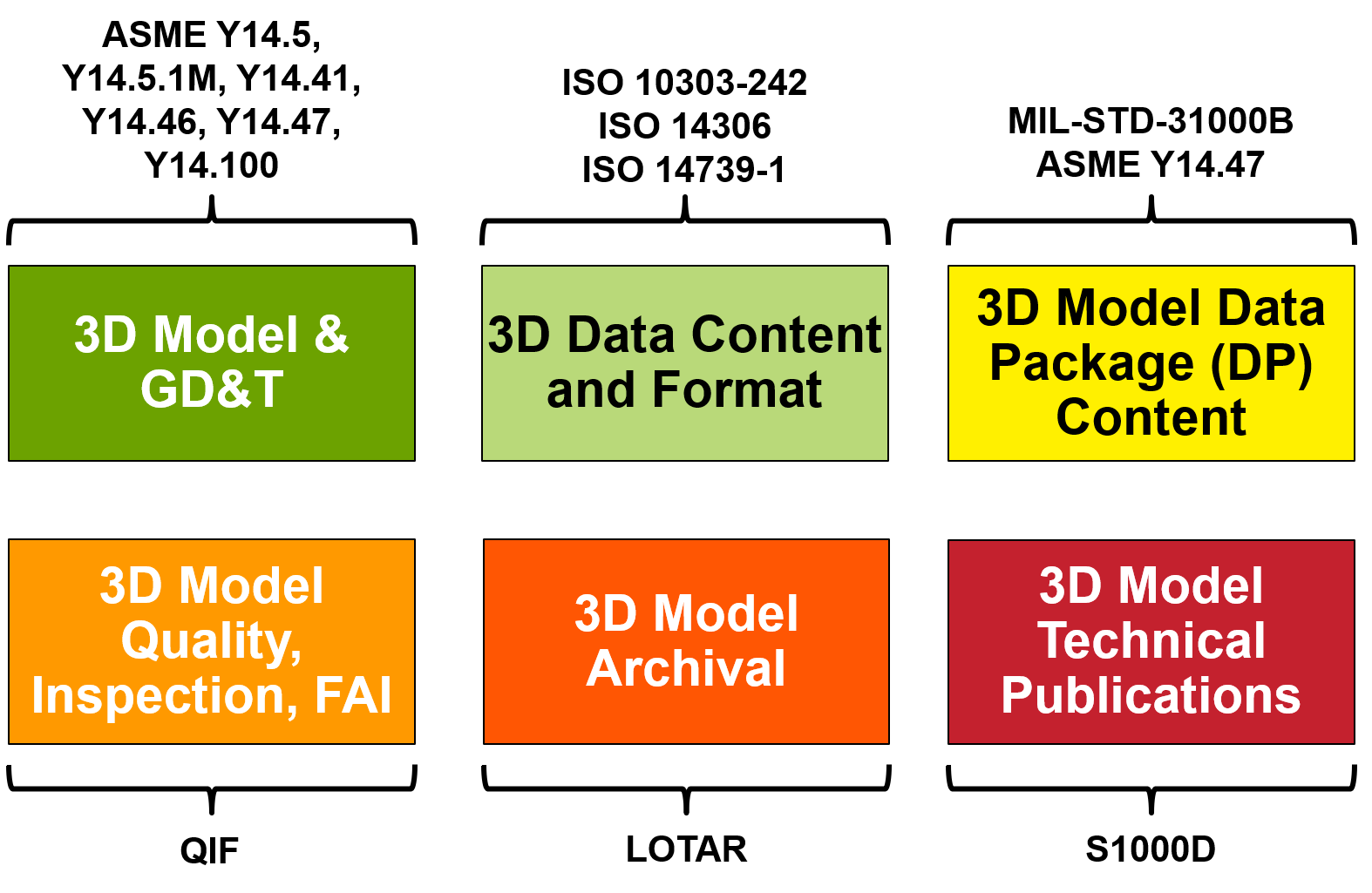 |
| Data that have been approved formally in accordance with the organizations data standardization procedures. |
| The process of developing and agreeing on (by consensus or decision) uniform engineering criteria for products, processes, practices, and methods for achieving compatibility, interoperability, interchangeability, or commonality of material. |
| Two or more parts that form a portion of an assembly or a unit replaceable as a whole but having a part or parts that are individually replaceable - e.g., gun mount stand, window sash, recoil mechanism, floating piston, telephone dial, Intermediate Frequency (IF) strip, terminal board with mounted parts. |  |
| A composite of equipment, skills, and techniques capable of performing or supporting an operational role or both. A complete system includes all equipment, related facilities, material, software, services, and personnel required for its operation and support to the degree that it can be considered a self- sufficient unit in its intended operational environment. |
| Entity responsible to establish, approve, and assess conformance to technical, safety, and certification requirements and policy for both products and processes. The term TA term can refer to the overall TA for a program or the TA for a specific engineering or technical discipline or design consideration. For example, the Federal Aviation Agency is the TA for civilian aircraft airworthiness and the USAF Technical Airworthiness Authority is the TA for Air Force aircraft airworthiness. |
| The logical traceability of the evolution of a systems data and models, decisions, and solutions throughout the lifecycle. |
| Recorded information of scientific or technical nature, regardless of form or character (such as equipment technical manuals and engineering drawings), engineering data, specifications, standards and Data Item Descriptions (DID). Data rights, data delivery, as well as use of any source controlled data as part of this element are included in technical data as are as maintained bills of material and system configuration identified by individual configuration item. Technical data does not include computer software or financial, administrative, cost or pricing, or management data or other information incidental to contract administration. |
| The authoritative technical description of an item. This technical description supports the acquisition, production, inspection, engineering, and logistics support of the item. The description defines the required design configuration and/or performance requirements, and procedures required to ensure adequacy of item performance. It consists of applicable technical data such as models, engineering design data, associated lists, specifications, standards, performance requirements, quality assurance provisions, software documentation and packaging details. | 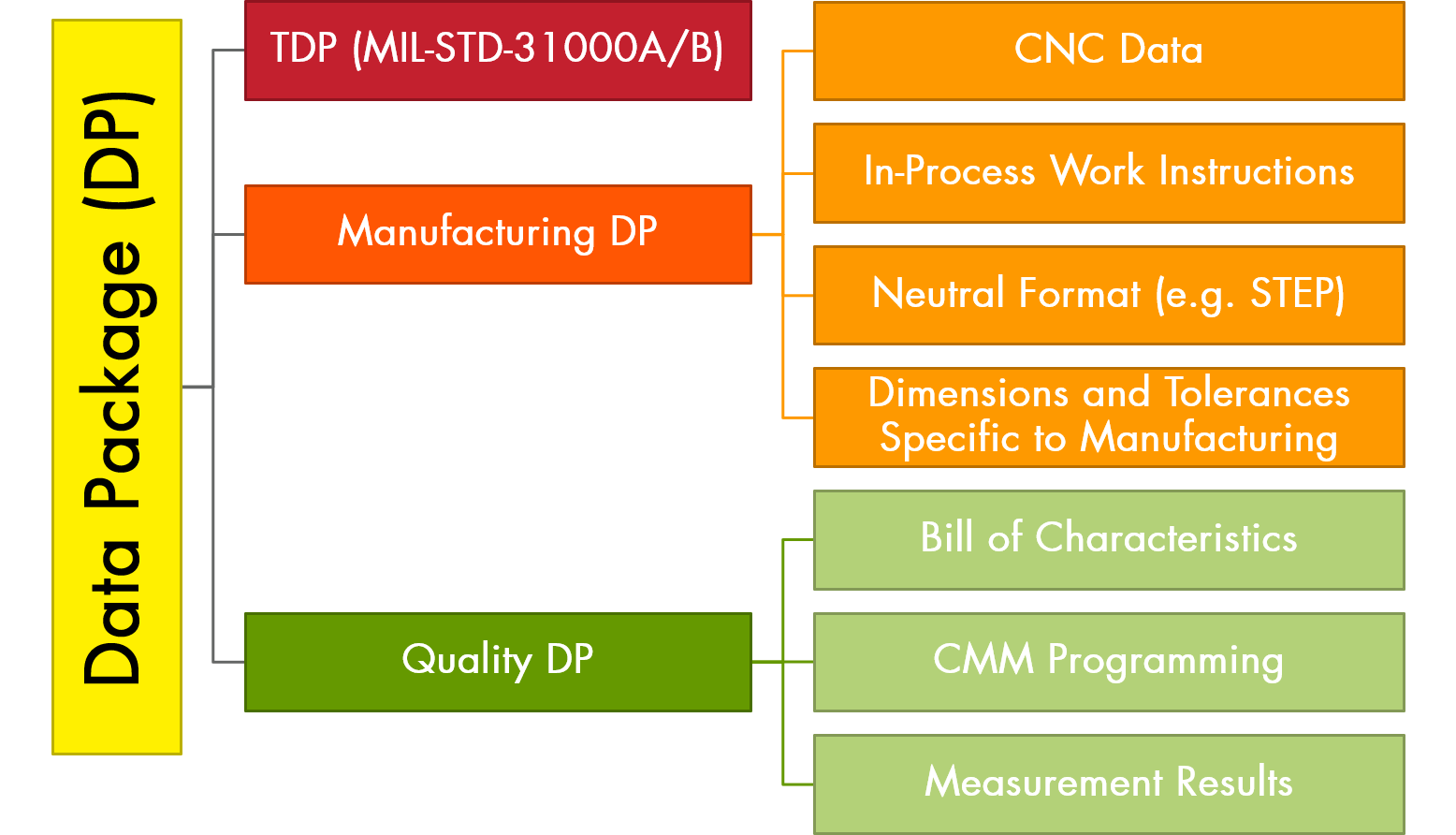 |
| Quantifiable attribute of both the systems development processes and status, as well as the systems product performance and maturity. TPMs are collected to provide information to Program Managers and Systems Engineers at routine intervals for decision making. |
| One level on a scale of 1 to 9, e.g., TRL 3, signifying technology readiness pioneered by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), adapted by the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL), and adopted by the Department of Defense as a method of estimating technology maturity during the acquisition process. The lower the level of the technology at the time it is included in a product development program, the higher the risk that it will cause problems in subsequent product development. |
| The total amount a dimension or feature is permitted to vary. The tolerance is the difference between the maximum and minimum limits. |
| Acronym For: Verification and Validation | 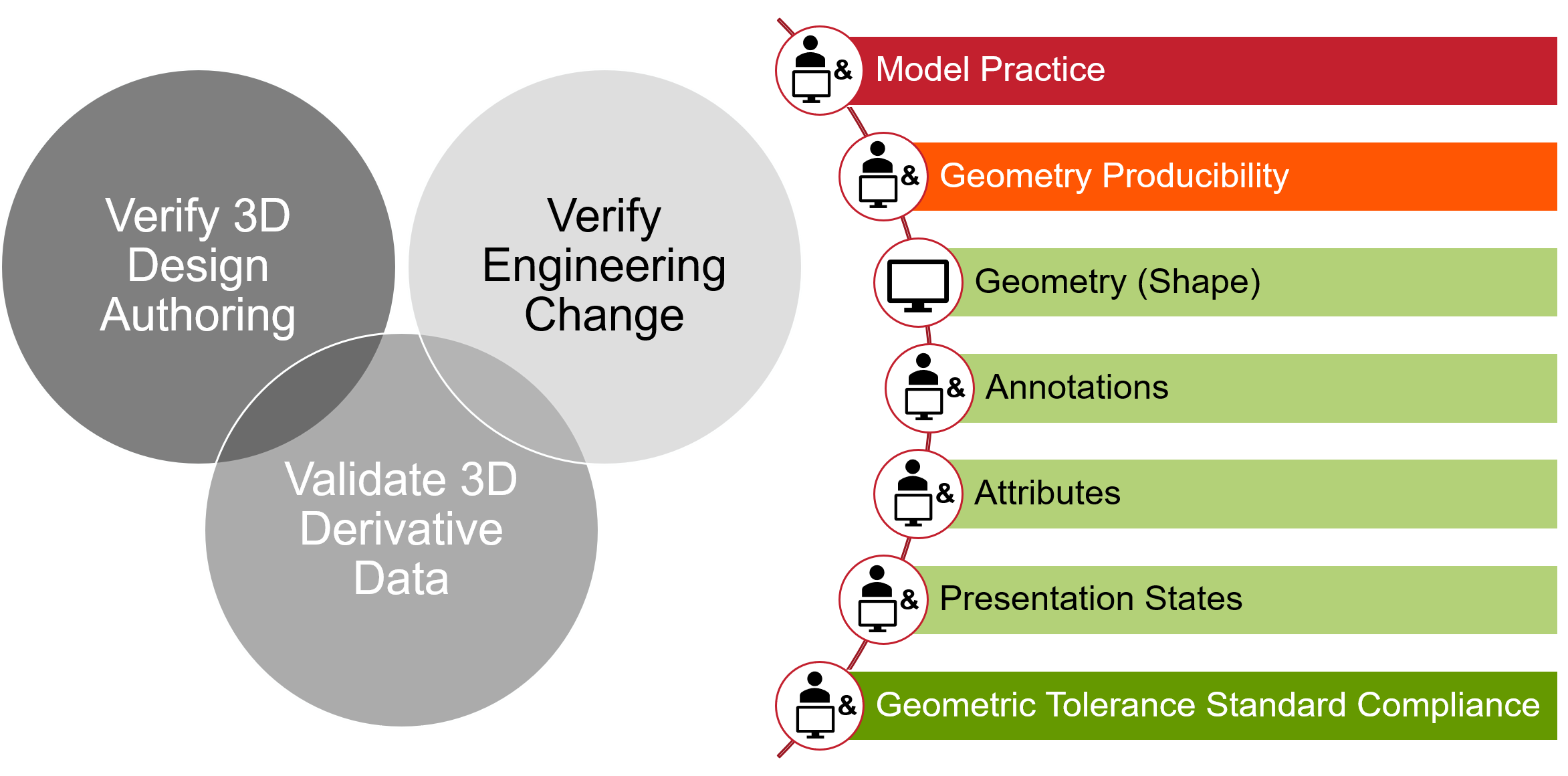 |
| An activity that assures that a product satisfies intent. |
| A source from whom a purchased item is obtained. |
| An activity that assures that a product satisfies requirements. |
| A group of related items that do not make up a complete assembly, with instructions for installing the items in a major assembly structure (e.g., a power supply and mounting hardware with instructions for installing them in a telecommunications satellite structure). |